Researchers on the Garvan Institute of Medical Analysis have uncovered how pancreatic most cancers hijacks an important metabolic “change” to assist it unfold, revealing a possible new therapy technique for this extremely aggressive illness.
The research, revealed in Science Advances, identifies the molecule Neuropeptide Y (NPY) as a key driver of pancreatic most cancers metastasis—the method by which most cancers spreads to different organs.
“NPY is a signaling molecule finest identified for its function in regulating metabolism, urge for food and satiety. We discovered NPY to be considerably greater in pancreatic most cancers cells in comparison with regular tissue,” says Dr. David Herrmann, senior creator of the research and Group Chief at Garvan.
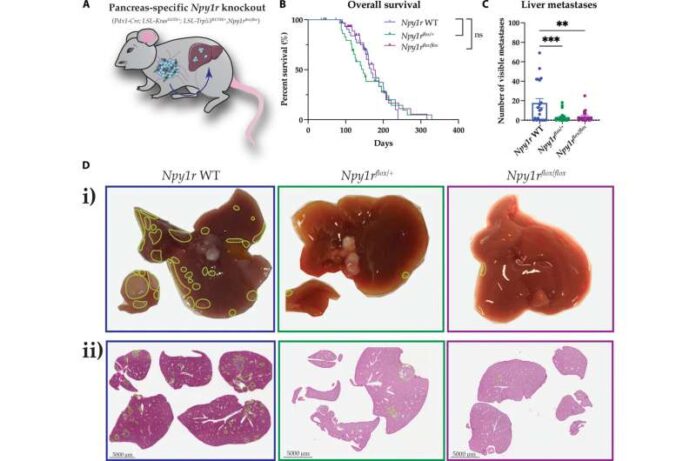
“By blocking NPY’s operate in mouse fashions, we discovered we may considerably cut back the unfold of pancreatic most cancers to the liver, the commonest website of metastasis in sufferers. These preliminary findings reveal this molecule as a promising goal to analyze additional for pancreatic most cancers.”
Slowing pancreatic most cancers
Pancreatic most cancers is without doubt one of the deadliest types of most cancers, with a median five-year survival fee of simply 13%. Greater than 80% of sufferers are identified at a complicated stage when surgical procedure is now not an choice. With metastasis a significant factor within the lethality of the illness, creating therapies that may stop most cancers from spreading is critically essential.
“Our analysis reveals that pancreatic most cancers hijacks a molecule identified for regulating physiological processes, resembling meals consumption and vitality stability, and makes use of it to advertise its personal unfold,” says first creator Dr. Cecilia Chambers, who accomplished the research as a Ph.D. researcher at Garvan.
“By blocking this molecule, we may decelerate pancreatic most cancers cell motion and metastatic outgrowth within the liver, thereby limiting the unfold of the most cancers.”
The research is the primary time the function of NPY has been investigated in pancreatic most cancers metastasis, constructing on earlier analysis that linked the molecule to most cancers development in breast, prostate and neuroblastoma cancers.
“Surprisingly, along with the anti-metastatic impact we noticed, blocking NPY additionally helped cut back the lack of muscle and fats tissue mass—often known as cachexia—that always accompanies most cancers development. This extra profit to keep up muscle and fats tissue could possibly be essential for sufferers to tolerate chemotherapy and different therapies,” says Dr. David Herrmann, senior creator of the research and Group Chief at Garvan.
New avenues for customized therapy
These findings may pave the way in which for extra focused therapies, explains Professor Paul Timpson, Head of the Invasion and Metastasis Lab at Garvan. “We discovered notably excessive ranges of NPY in extremely aggressive and metastatic pancreatic cancers. This means that blocking NPY could possibly be an efficient customized therapy for this subset of sufferers, in addition to those that expertise extreme weight reduction resulting from most cancers.”
Following their promising findings, the researchers developed an antibody designed to neutralize NPY’s impact in most cancers, which they’re now testing in mouse fashions and in tissues donated by pancreatic most cancers sufferers.
Transferring discovery towards scientific trials
Whereas the research offers preliminary proof that inhibiting NPY could cut back most cancers unfold and cut back weight reduction, the analysis staff is now working to optimize how this technique could possibly be mixed with present therapies.
“One among our subsequent steps is to refine how we use this method together with chemotherapy,” says Dr. Herrmann.
“There’s rising proof that timing is crucial—thus figuring out whether or not NPY inhibition is handiest when launched earlier than or after chemotherapy is essential. Understanding this might be key to translating our findings into scientific trials, and finally to enhance the outcomes of this illness.”
Extra data:
Cecilia R. Chambers et al, Focusing on the NPY/NPY1R signaling axis in mutant p53–dependent pancreatic most cancers impairs metastasis, Science Advances (2025). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq4416
Quotation:
A metabolic ‘change’ that would assist cease the unfold of pancreatic most cancers (2025, March 14)
retrieved 14 March 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2025-03-metabolic-pancreatic-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.